The Response > Regional ballast water strategies
Addressing IAS requires coordinated responses between nations and especially between nations closely connected geographically and/or through trade and travel. Under the GloBallast Partnerships Programme, Regional Strategies and Action Plans for BWM are being developed in all affiliated regions, through the Regional Task Forces and in the framework of the UNEP Regional Seas Programme.
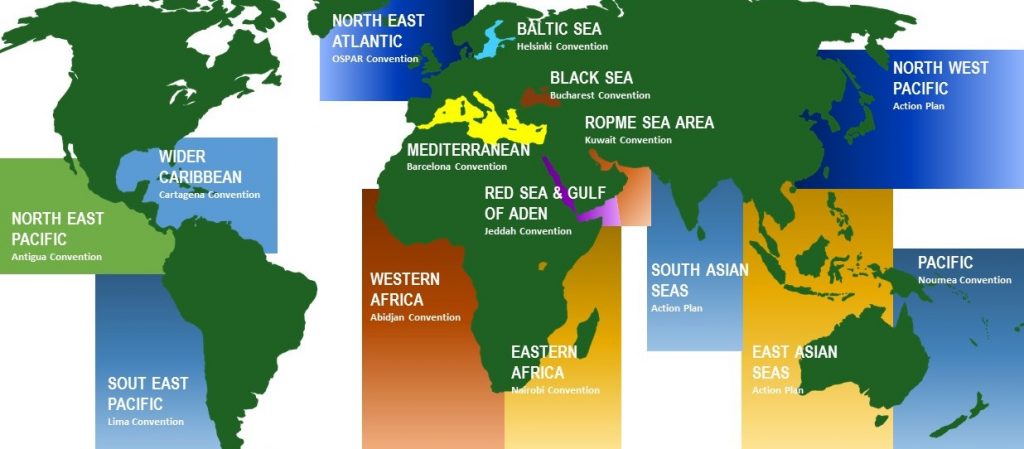
UNEP Regional Seas Programme
The UNEP Regional Seas Programme was launched in 1974 in the wake of the 1972 United Nations Conference on the Human Environment (UNCHE) held in Stockholm. It aims to address the accelerating degradation of the world’s oceans and coastal areas through the sustainable management and use of the marine and coastal environment, by engaging neighbouring countries in comprehensive and specific actions to protect their shared marine environment. Today, more than 140 countries participate in 13 Regional Seas Programmes established under the auspices of UNEP: the Black Sea, Wider Caribbean, East Africa, South East Asia, ROPME Sea Area, Mediterranean, North-East Pacific, North-West Pacific, Red Sea and Gulf of Aden, South Asia, South-East Pacific, South Pacific, and West and Central Africa. Furthermore, five partner programmes for the Antarctic, Arctic, Baltic Sea, Caspian Sea and North-East Atlantic Regions are members of the Regional Seas family.
All the programmes under the aegis of the UNEP Regional Seas Programme are supported by regional conventions and associated protocols on specific problems. They function through action plans covering issues ranging from chemical wastes and coastal development to the conservation of marine animals and ecosystems. IAS issues, including ballast water management, have relatively easily been incorporated into the agreements by means of technical protocols, thereby offering an ideal platform for implementation of the Ballast Water Management Convention. Such protocols should obviously be consistent with the provisions of the International Convention on Ballast Water Management.
Examples of regional strategies for BWM
WIDER CARIBBEAN
The Regional Strategic Action Plan to Minimize the Transfer of Harmful Aquatic Organisms and Pathogens in Ships’ Ballast Water and Sediments Wider Caribbean Region was prepared and adopted by the Regional Task Force in 2012. The strategy was endorsed by the 15th Inter Governmental Meeting (IGM) for the Cartagena Convention in October 2012.
MEDITERRANEAN
The Mediterranean Strategy on Ships’ Ballast Water Management was prepared and developed by the Regional Task Force over the period 2008-2011 and adopted by the 17th Ordinary Meeting of the Contracting Parties to the Barcelona Convention (Paris, France, February 2012). The Regional Strategy includes:
- a set of eight strategic priorities and actions concerning ballast water management in the region;
- an action plan and implementation timetable (2011-2015);
- harmonized voluntary temporary arrangements for ballast water exchange in the Mediterranean (applicable as from 1 January 2012 following formal support of Mediterranean States) – IMO Circular BWM.2/Circ.35;
- a regional system for compliance, monitoring and enforcement; and
- a structure for a regional information system on invasive species, ports at risk, etc.
Regional Coordination Organization: REMPEC
WEST AND CENTRAL AFRICA
The West and Central Africa Regional Strategic Action Plan (SAP) to Minimize the Transfer of Harmful Aquatic Organisms and Pathogens in Ships` Ballast Water was adopted in Abidjan, Cote d’Ivoire, in 2009 and revised in Lomé, Togo, in 2011. It is not yet adopted by the Abidjan Convention.
RED SEA AND GULF OF ADEN
In 2011, the Regional Task Force prepared the Red Sea and Gulf of Aden Regional Strategic Action Plan for the Control of Transfer of Harmful Aquatic Organisms and Pathogens in Ships’ Ballast Water. The legal regional framework was reviewed and adopted in 2014, and incorporated into the existing Regional Convention for the Conservation of the Red Sea and Gulf of Aden Environment, known as the Jeddah Convention.
Regional Coordination Organization: PERSGA
SOUTH EAST ASIA
The regional strategy was drafted in Singapore in 2012 and reviewed by the 25th Maritime Transport Working Group Meeting in Myanmar in March 2013. It was updated in November 2015, during a meeting in Bangkok.
Lead Regional Agency: ASEAN MTWG
SOUTH EAST PACIFIC
The Regional Strategy for Ballast Water Management in the Southeast Pacific countries and Argentina and its Plan of Action were developed during the Second Meeting of the Regional Task Force held in Buenos Aires, Argentina, in September 2009. It was later adopted by the XVI Meeting of the Parties to the Lima Convention in Guayaquil, Ecuador on 22 January 2010.
Regional Coordination Organization: CPPS
SOUTH PACIFIC
Regional Strategy for Shipping Related Invasive Marine Pests in the Pacific (SRIMP-PAC). This strategy is pending adoption.
Lead Regional Agency: SPREP
BLACK SEA
The draft regional strategy for ballast water management in Black Sea: road map for the BWM Convention ratification, guidelines and action plan, was adopted in 2009 Bucharest Convention.
CASPIAN SEA
The Regional Strategy and Action Plan on Ballast Water Management for the Caspian Sea was developed and reviewed at a workshop, organized by IMO in Baku, Republic of Azerbaijan, from 9 to 11 July 2012. It was endorsed by the COP of the Tehran Convention in Moscow in December 2012.
BALTIC / NORTH SEA
The Contracting Parties to the Barcelona Convention, the OSPAR Convention and the HELCOM Convention agreed on the voluntary interim application of the Ballast Water Exchange Standard D-1 by vessels operating between the Mediterranean Sea and the North-East Atlantic and/or the Baltic Sea, applicable from 1 October 2012 (BWM.2/Circ. 39).
Lead Regional Agency: HELCOM / OSPAR / Barcelona Conventions
ROPME SEA REGION (RSA)
The Regional Strategic Action Plan (SAP) to implement the Ballast Water Management Convention and Associated Guidelines to Minimize the Transfer of Harmful Aquatic Organisms and Pathogens in Ships’ Ballast Water in the ROPME Sea Area was adopted by the ROPME Council in 2008. Further developments have been the designation of BW Exchange Areas (MEPC 59/INF.3) and the implementation of BW Reporting Form (MEPC 60/INF.2).
SOUTH ASIA
Draft strategy reviewed in May 2012. To be further developed by SACEP at a follow-up meeting in 2014.
Lead Regional Agency: SACEP
You can read more about regional IAS agreements in GloBallast Monograph 18.




