More information and download links below the graphic.
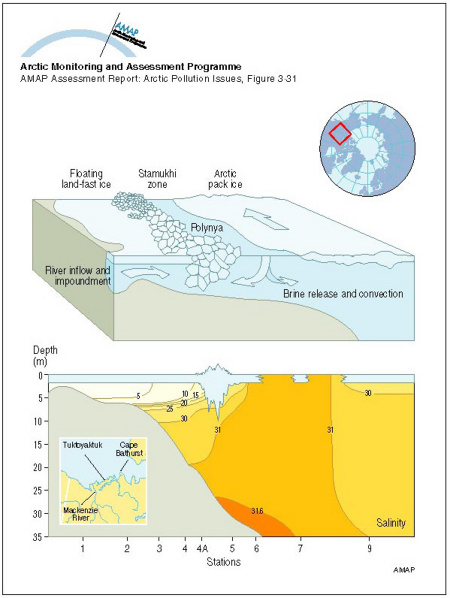
A schematic diagram showing the inflow from the Mackenzie River trapped in the nearshore zone beneath the landfast ice Beyond the stamukhi zone, intermittent opening and refreezing in the flaw lead produces brine which encourages mixing and convection
Click here, or on the graphic, for full resolution.
A schematic diagram showing the inflow from the Mackenzie River trapped in the nearshore zone beneath the landfast ice Beyond the stamukhi zone, intermittent opening and refreezing in the flaw lead produces brine which encourages mixing and convection
| Sources | Title (cont.) Numbers in lower panel are salinity values. Macdonald, R.W. and E.C. Carmack, 1991. The role of large-scale under-ice topography in separating estuary and ocean on an Arctic shelf. Atmosphere-Ocean 29(1): 37-53. (AAR Figure 3.31) | ||||
|
Cartographer/ Designer |
Graphical production: Philippe Rekacewicz and Emmanuelle Bournay (GRID-Arendal) | ||||
| Appears in |
AMAP Assessment Report: Arctic Pollution Issues |
||||
| Published | 1998 | ||||
| Feedback/Comment/Inquiry | Contact webmaster | ||||
| Search for other graphics |
With related subjects Covering the same geographic area |
||||
|
Available Downloads
(please review use constraints above) |
|
||||
|
Citation/Reference Use constraints |
Please refer to the AMAP policy regarding use and reproduction of AMAP maps and graphics |