Your query returned 93 graphics.
Results 46 - 60
Circumpolar age-standardized mortality rates by cause per 100 000 personsCircumpolar age-standardized mortality rates by cause per 100 000 persons; standardized to European Standard Population |
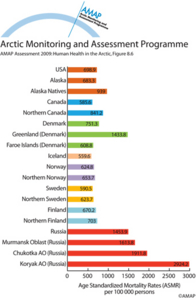
|
Different types of biomarker in the pathogenic sequence between exposure and diseaseDifferent types of biomarker in the pathogenic sequence between exposure and disease |
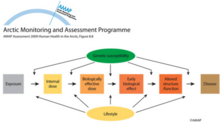
|
POPs related xenobiotic serum activities in Inuit and combined European study groups (a)POPs related xenobiotic serum activities in Inuit and combined European study groups (a) agonistic serum xenoestrogenic activity. * indicates significant difference vs Europeans at p < 0.05. |
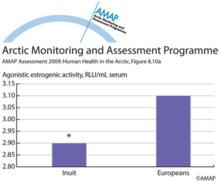
|
POPs related xenobiotic serum activities in Inuit and combined European study groups (b)POPs related xenobiotic serum activities in Inuit and combined European study groups (b) agonistic serum xenoandrogenic activity. * indicates significant difference vs Europeans at p < 0.05. |
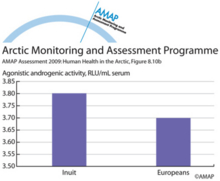
|
POPs related xenobiotic serum activities in Inuit and combined European study groups (c)POPs related xenobiotic serum activities in Inuit and combined European study groups (c) serum AhR activity. * indicates significant difference vs Europeans at p < 0.05. |
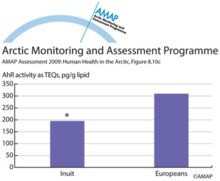
|
POPs related xenobiotic serum activities in Inuit and combined European study groups (d)POPs related xenobiotic serum activities in Inuit and combined European study groups (d) sperm DNA damage. * indicates significant difference vs Europeans at p < 0.05. |
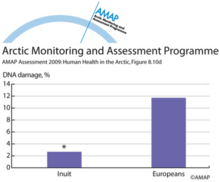
|
POPs related xenobiotic serum activities in Inuit and combined European study groups (e)POPs related xenobiotic serum activities in Inuit and combined European study groups (e) sperm DNA fragmentation index. * indicates significant difference vs Europeans at p < 0.05. |
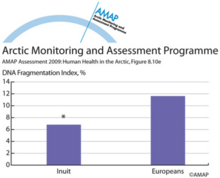
|
The various elements of the risk assessment processThe various elements of the risk assessment process |
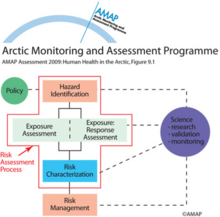
|
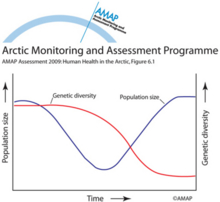
Relationship between genetic diversity and population numbersRelationship between genetic diversity and population numbers |
|
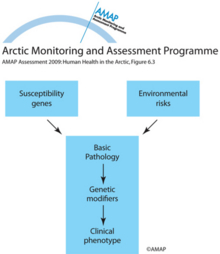
The paradigm of interactions between genes and environment and development of a clinical phenotypeThe paradigm of interactions between genes and environment and development of a clinical phenotype |
|
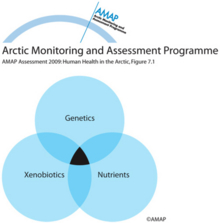
Genes, macronutrients, and contaminants may have synergistic effects on the development of diseasesGenes, macronutrients, and contaminants may have synergistic effects on the development of diseases. The probability for illness is increased when several pre-disposing factors are simultaneously [..] |
|
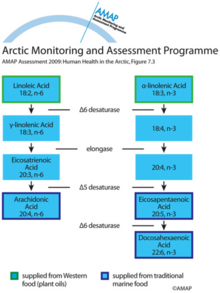
Metabolism of polyunsaturated fatty acidsMetabolism of polyunsaturated fatty acids |
|
Effects of PPAR- α, PPAR-β/δ, and PPAR-γ in various tissuesEffects of PPAR- α, PPAR-β/δ, and PPAR-γ in various tissues |
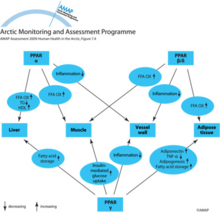
|
Interactions between the uric acid formation pathway and dietary and environmental factorsInteractions between the uric acid formation pathway and dietary and environmental factors |
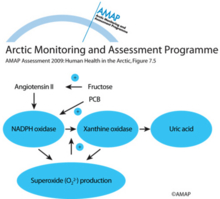
|
Effect of mercury and dioxin-like compounds on the pathogenesis of diabetes and its complicationsEffect of mercury and dioxin-like compounds on the pathogenesis of diabetes and its complications |
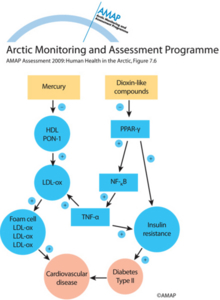
|
water OR waste searches for either of these words
oceans AND biodiversity searches for blocks with both words
pollution NEAR water searches for blocks with either of these words, with them being closer ranks higher
"climate change" searches for this phrase